Appearance
Selecting Single or Multiple Values
Selecting values from a drop-down menu is faster than typing them in manually and it also ensures that there are no typos or spelling variations. Additionally, it is possible to create drill-down (cascade) forms, where a value selected in one field can affect the options available in another field.
Widget | Preview in the mobile app |
|---|---|
| Drop-down menu with predefined values |  |
| Drop-down menu with values from another table, allowed multiple selection |  |
To select values from a drop-down menu in the form, you can use the Value Map or Value Relation widgets in QGIS. The field data type depends on the values that should be stored in the field, usually Text (string) or Integer. To allow multiple selection, the field needs to be of Text (string) data type).
The Value Relation widget is a bit more complex as it uses another layer (usually a non-spatial table) as a source of values. However, it provides some benefits when compared to the simpler Value Map setup, such as:
- Option to select multiple values from the list
- The table used for the drop-down menu can be edited in the mobile app. For example, if there is a value missing, you can create it during the field survey and use it immediately. The Value Map options can be managed only through QGIS.
- Searching the values: if you have a large list of values, it will become cumbersome to find the right value. With the Value Relation widget, you have the option to search for values in the list in the mobile app.
Example projects available
The public project documentation/form-widgets contains both Value Map and Value relation widgets. Download or clone it to see the setup.
Drill-down forms are included in documentation/form_setup public project.
Value Map
Value map widget is used to select a value from a drop-down menu. Values are defined in the widget in layer properties in QGIS. They cannot be changed or added from the mobile app. Only one value can be selected.
If you want to use multiple selections in a field or need to add new values during the survey, check out the Value Relation widget.
Example project available
This public project documentation/form-widgets contains a Value Map field. Download or clone it to see the setup.
Prefer a video? Here is a short tutorial about using Value Map widget:
- Right-click on a layer, select Properties and go to the Attributes form tab.
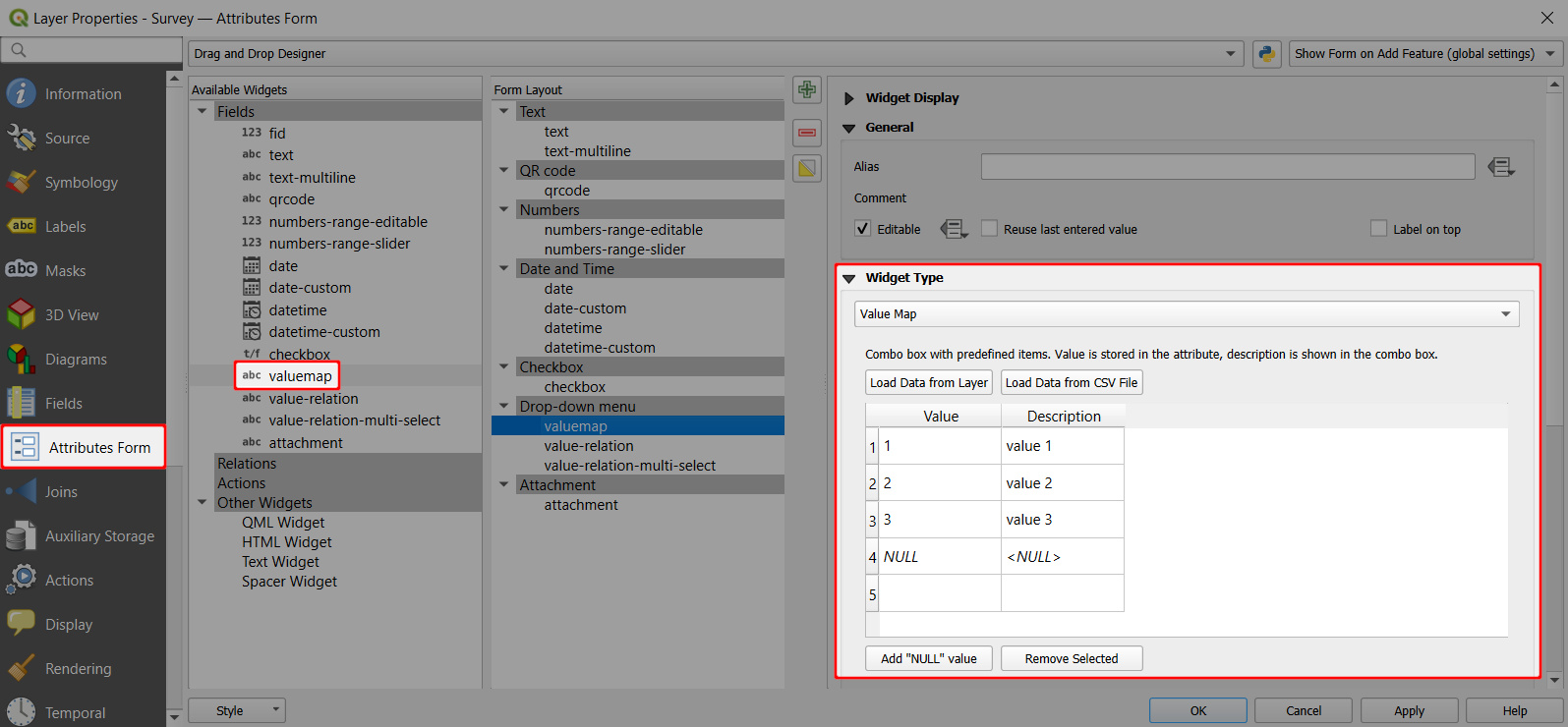
- In the list of Available Widgets select the field you want to work with (here:
valuemap) - In the Widget Type tab, select the Value Map option from the drop-down menu and fill in the table below. Value is what will be stored in the field (these can be coded values or shortened names, here we use
1,2,3). Description is what will be displayed in the form and in the attributes table (here:value 1,value 2,value 3). - Apply the changes. Don't forget to save and sync your project!
Now you can select the value from a drop-down menu in the mobile app: 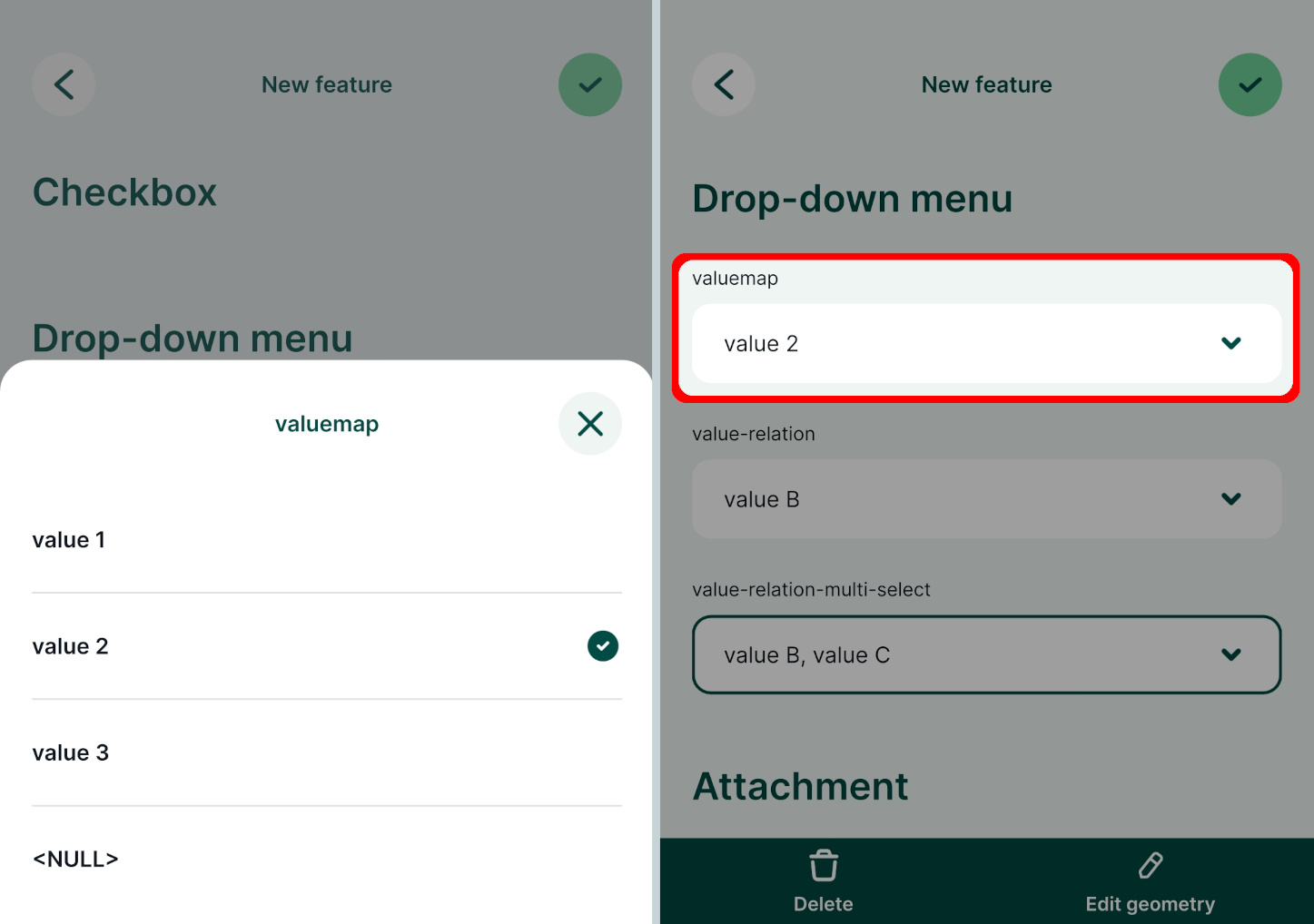
Value Relation
The Value Relation widget is similar to the Value Map widget, but the values for the drop-down menu come from another layer (usually a non-spatial table).
Example project available
This public project documentation/form-widgets contains a Value Relation setup. Download or clone it to explore it in more detail.
Prefer a video? Here is a short tutorial about using Value relations:
To have the option to safely add new values when working collaboratively, the value table should have a unique field with UUID values. This field should use the uuid() function as a default value, so that every new entry has its UUID.
To set up Value Relation in QGIS:
- Right-click on a layer, select Properties and go to the Attributes form tab.
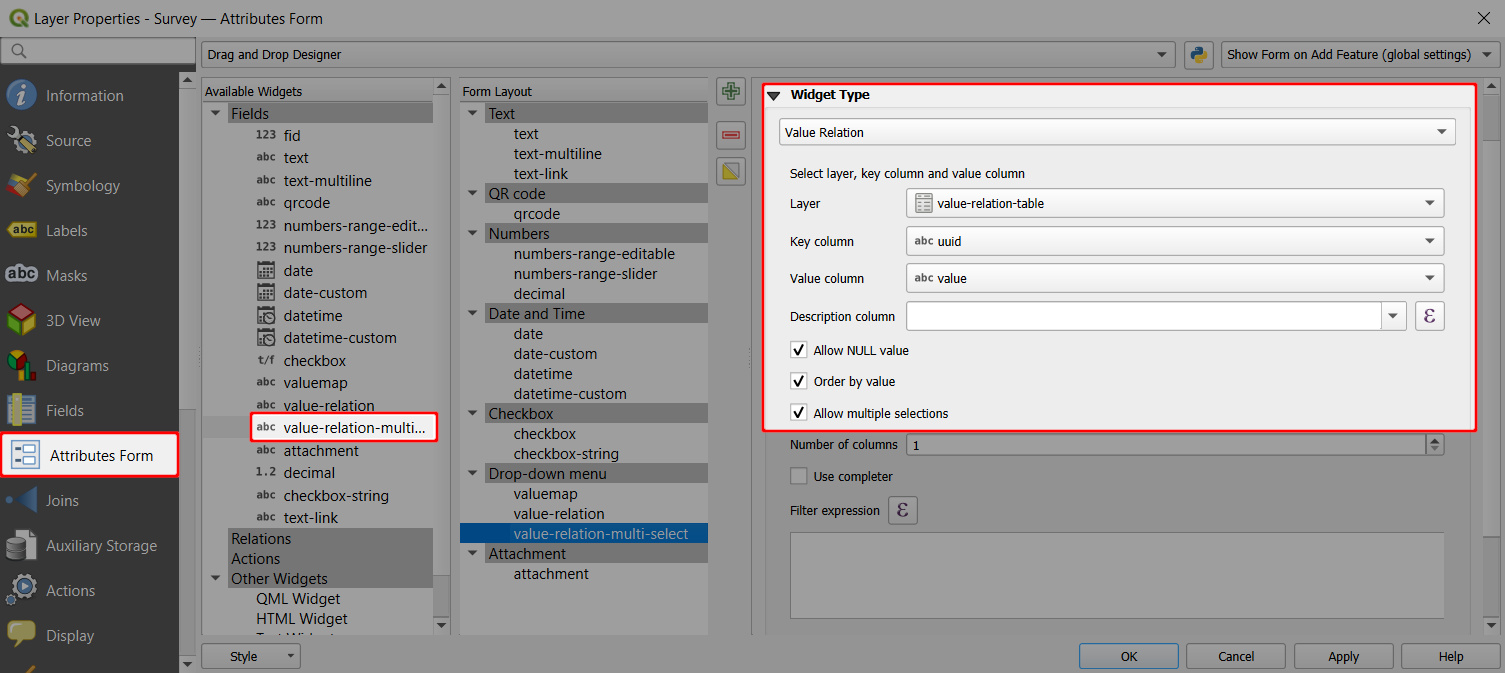
- In the list of Available Widgets select the field you want to work with (here:
value-relation-multi-select) - In the Widget Type tab, select Value Relation from the drop-down menu and set it up as follows:
- Select the Layer that contains the values (here:
value-relation-table) - Key column is the field that contains the values (here:
uuid) - Value column is the field that contains the alias (description) of the value (here:
value) - Check the Allow multiple selections option ✔️ if you want to have the option to select multiple values
- Select the Layer that contains the values (here:
- Apply the changes. Don't forget to save and sync your project!
Using UUID as key field
Why UUID? FID can be changed during synchronisation. If multiple surveyors add new entries to the value table, features can end up with wrong values.
On the other hand, UUID (Universally Unique Identifier) is guaranteed to be unique and will not be changed when synced. Therefore, we recommend using UUID if you want to add new values during the survey.
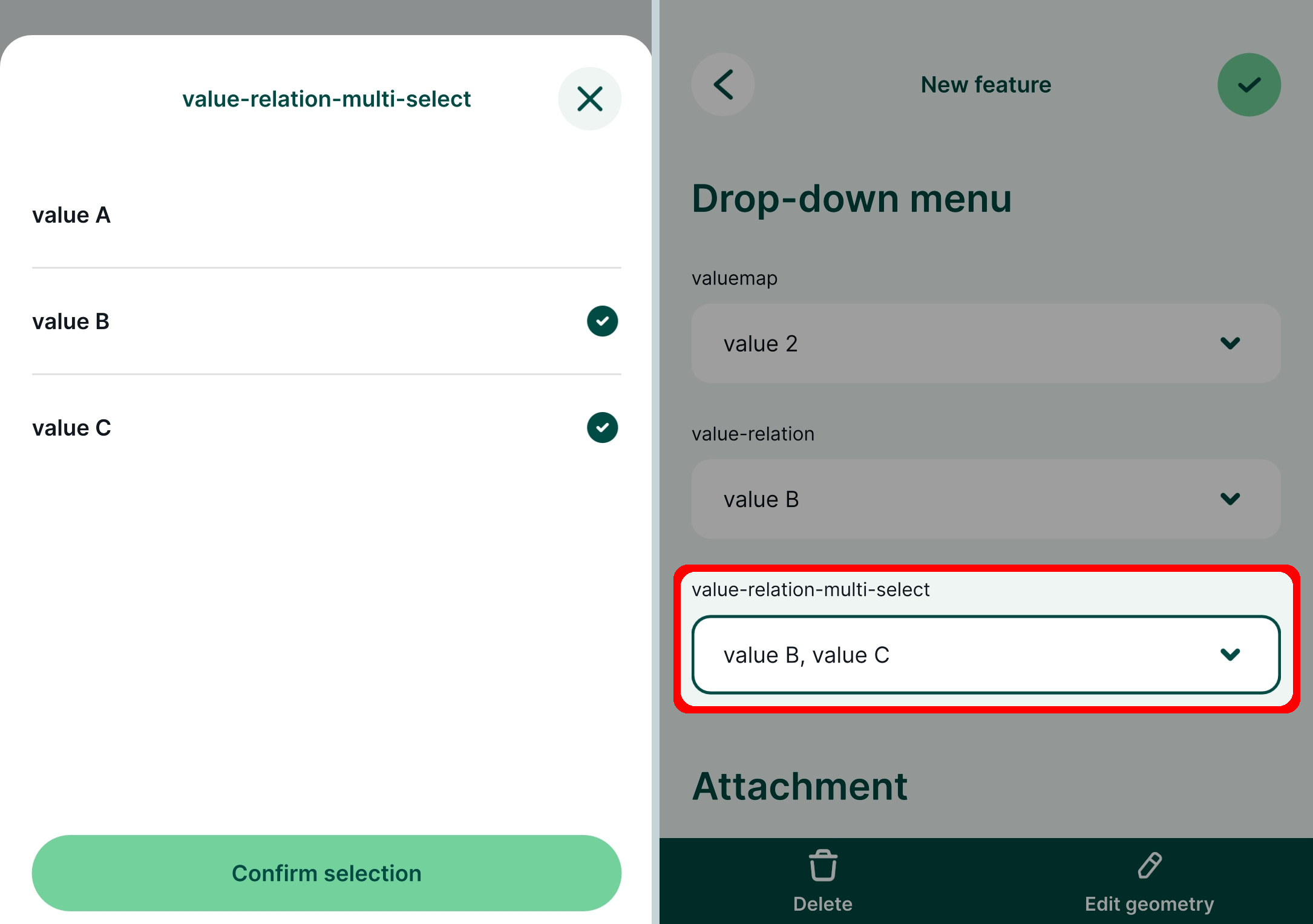
When you open the field with Value Relation in the mobile app, you will be able to select a value or multiple values from the list.
Drill-down forms
Drill-down or cascade forms enable to list values in a field depending on a value selected in another field.
Example project available
Clone documentation/form_setup to explore drill-down forms.
Prefer a video? Here is a short tutorial about drill-down forms:
How to set up drill-down forms
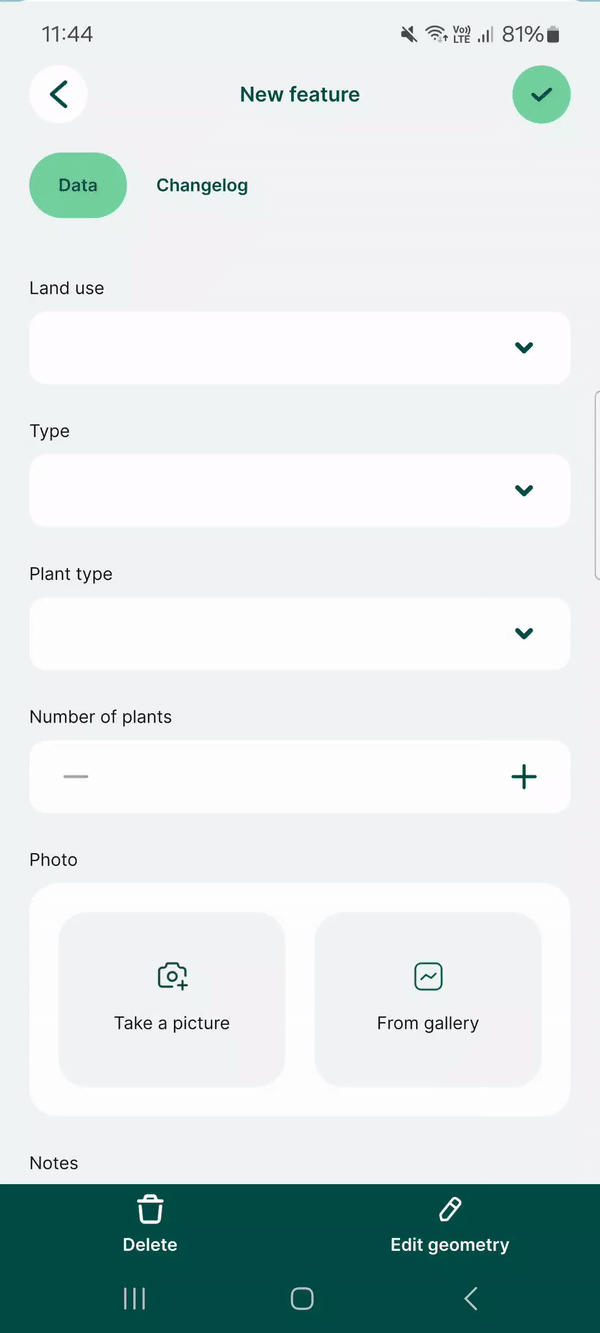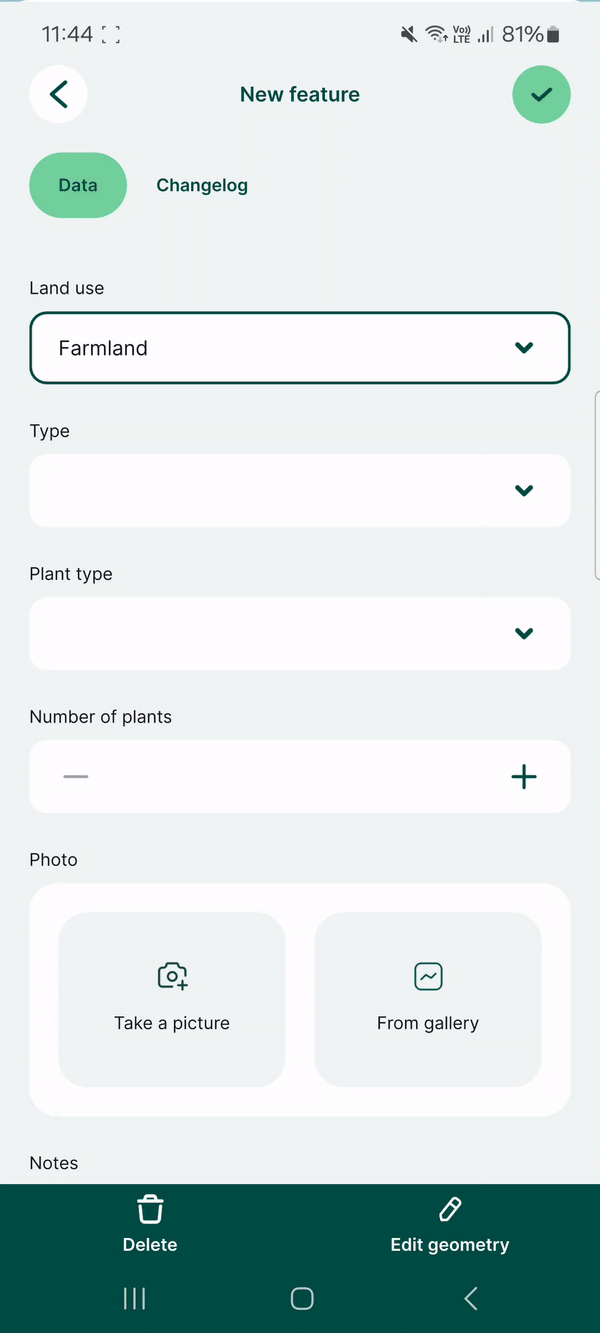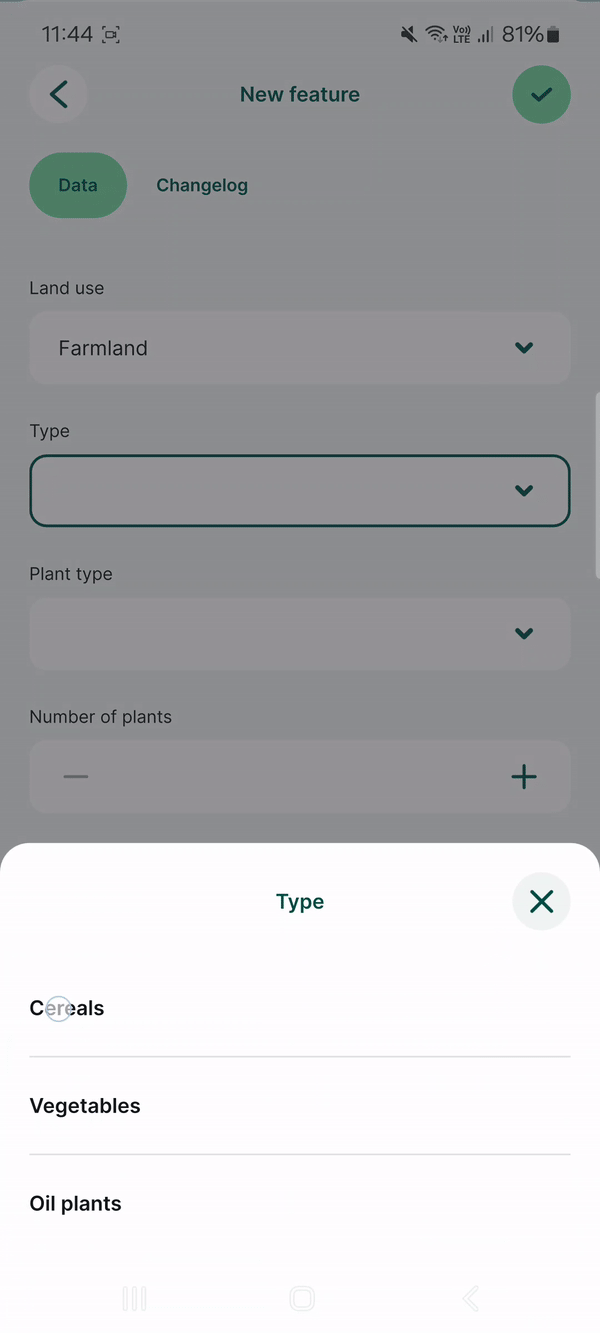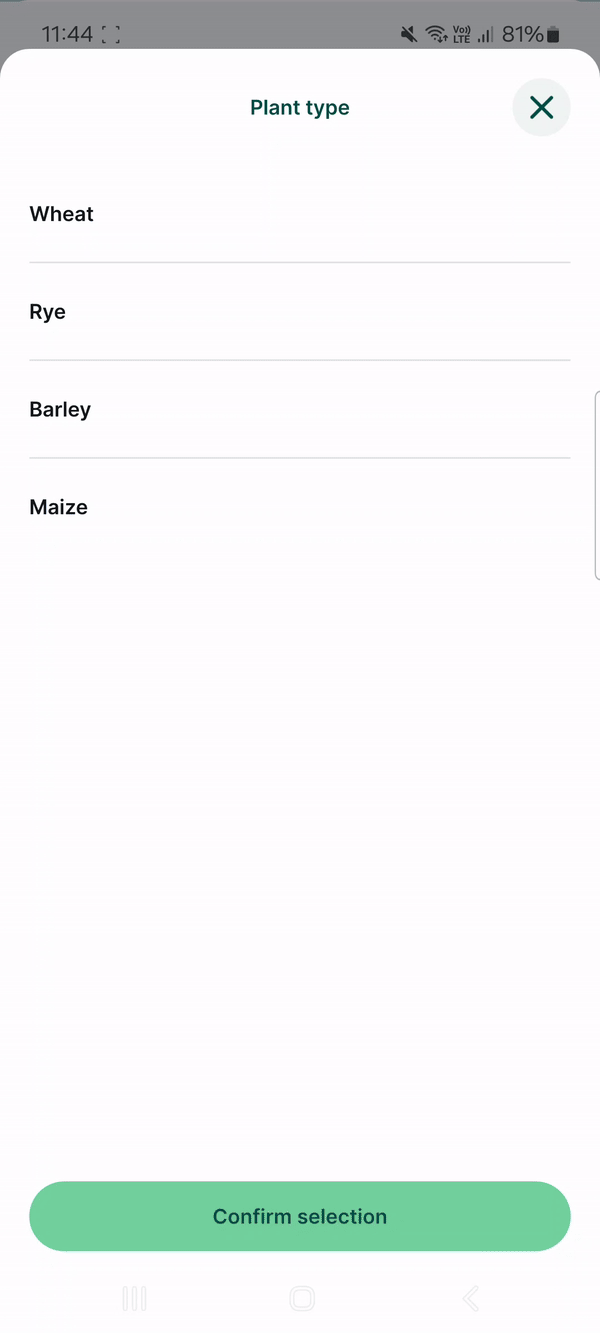
Here, we have a layer named landuse that has fields such as Land use, Type, Plant type. Values that can be filled in these fields depend on the previous choices: if we select Farmland as the Land use, the Type field drop-down menu offers options such as Cereals, Oil plants or Vegetables. Subsequently, the Plant type field has only options that are relevant for the selected type of land use.
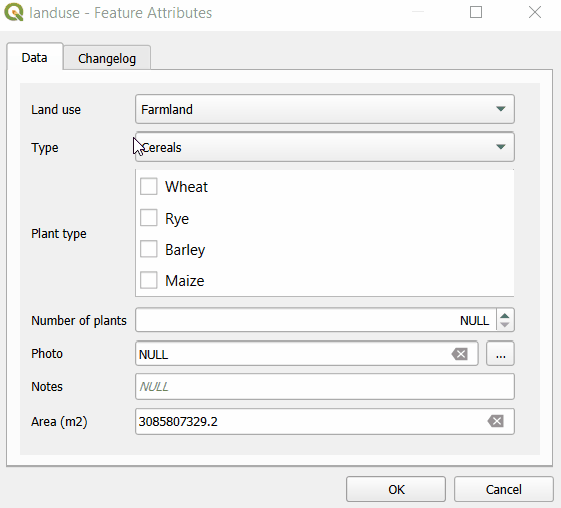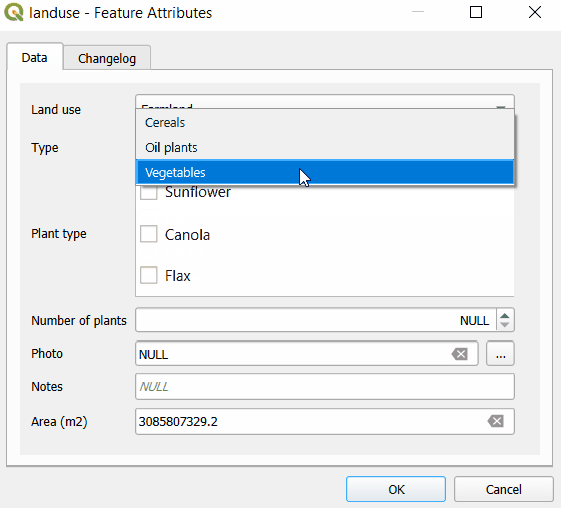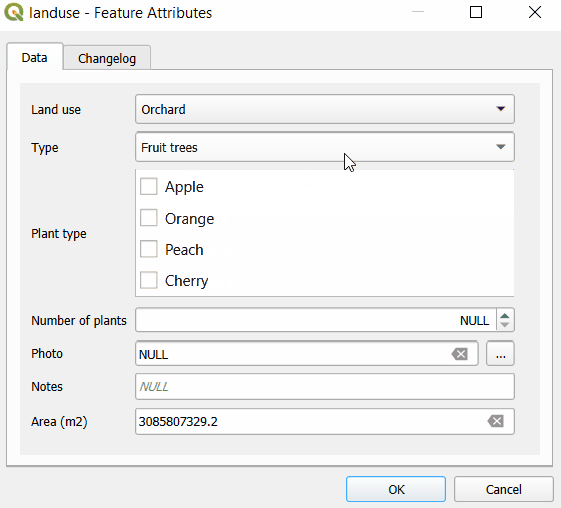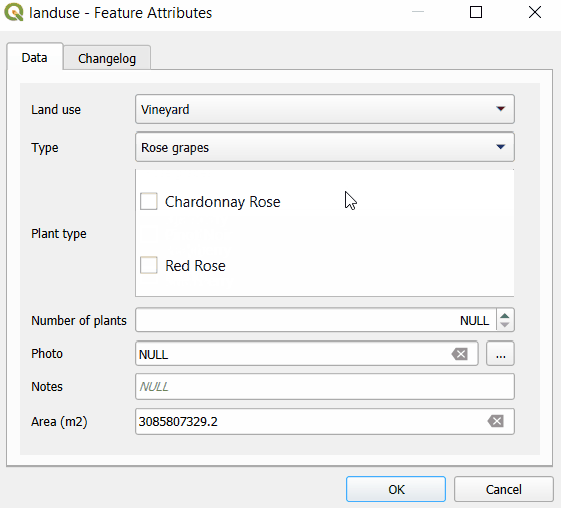
First, let us explore the structure of value tables that are used to set up drill-down forms. In the example project, Land use field uses plant-habitat value table that has following fields:
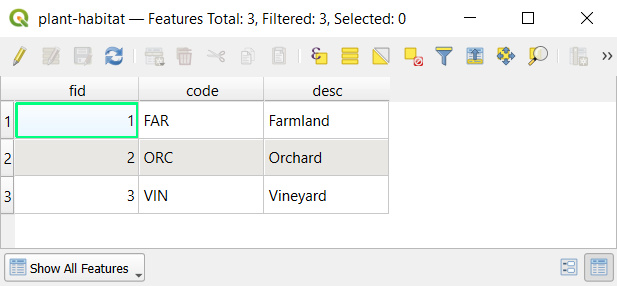
The Type field refers to the plant-type value table. In this table, there is a field habitat-code that refers to a specific code value from the plant-habitat table. For instance, the FAR habitat code (standing for Farmland) is used as the habitat-code for Cereals, Vegetables, Oil plants as these are applicable farmland types.
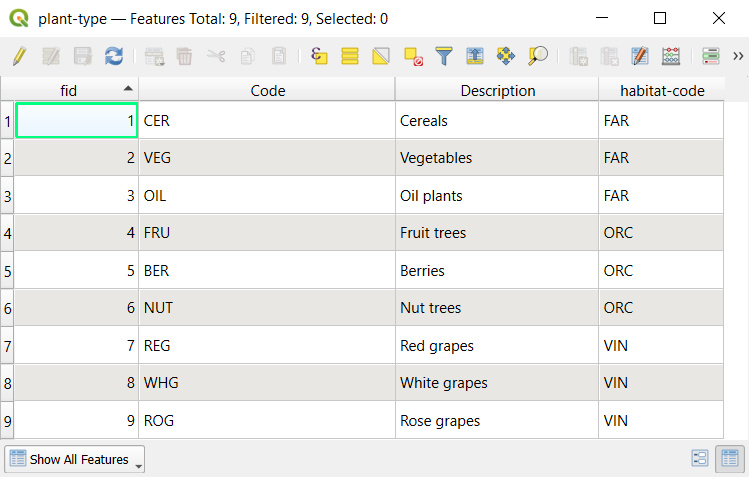
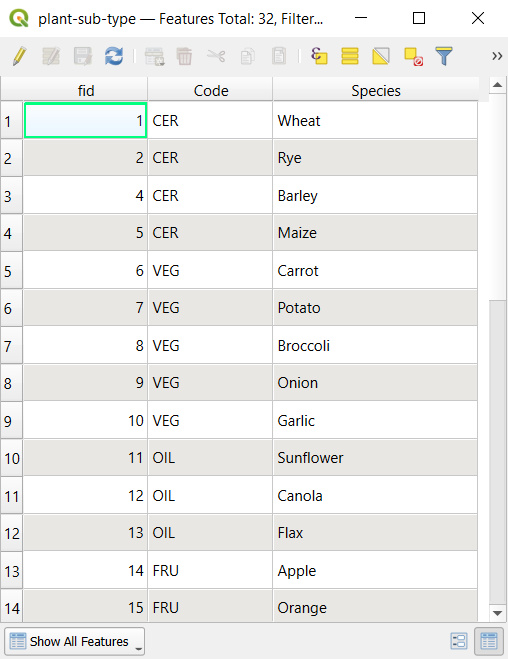
Similarly, the Plant type field uses the plant-sub-type value table that contains a Code field that refers to specific types from the plant-type table. For instance, the CER type code is applied for Wheat, Rye, Barley, Maize, meaning these types of plants belong to the Cereals category.
To set up drill-down forms:
Right-click on a survey layer, select Properties and go to the Attributes form tab
The
habitatfield aliased as Land use is set up using the Value relation widget. Values are defined in theplant-habitattable:- Key column is the field that contains the values (here:
code) - Value column is the field that contains the alias (description) of the value (here:
desc)
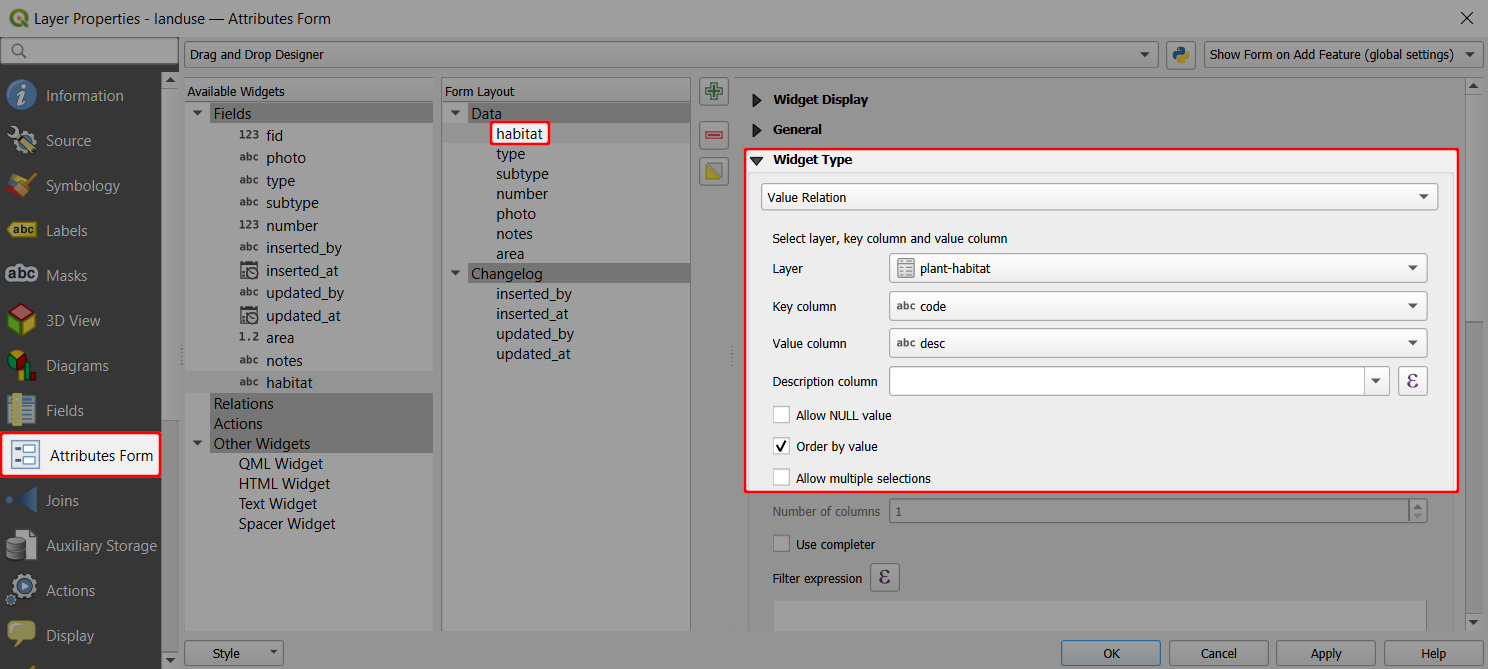
- Key column is the field that contains the values (here:
The
typefield (aliased as Type) uses the Value relation widget with values from theplant-typetable:- Key column is the field that contains the values (here:
Code) - Value column is the field that contains the alias (description) of the value (here:
Description) - Filter expression:
"habitat-code"= current_value('habitat')is used to limit the options in the drop-down menu to values where thehabitat-codeof the value is the same as the current value of thehabitatfield.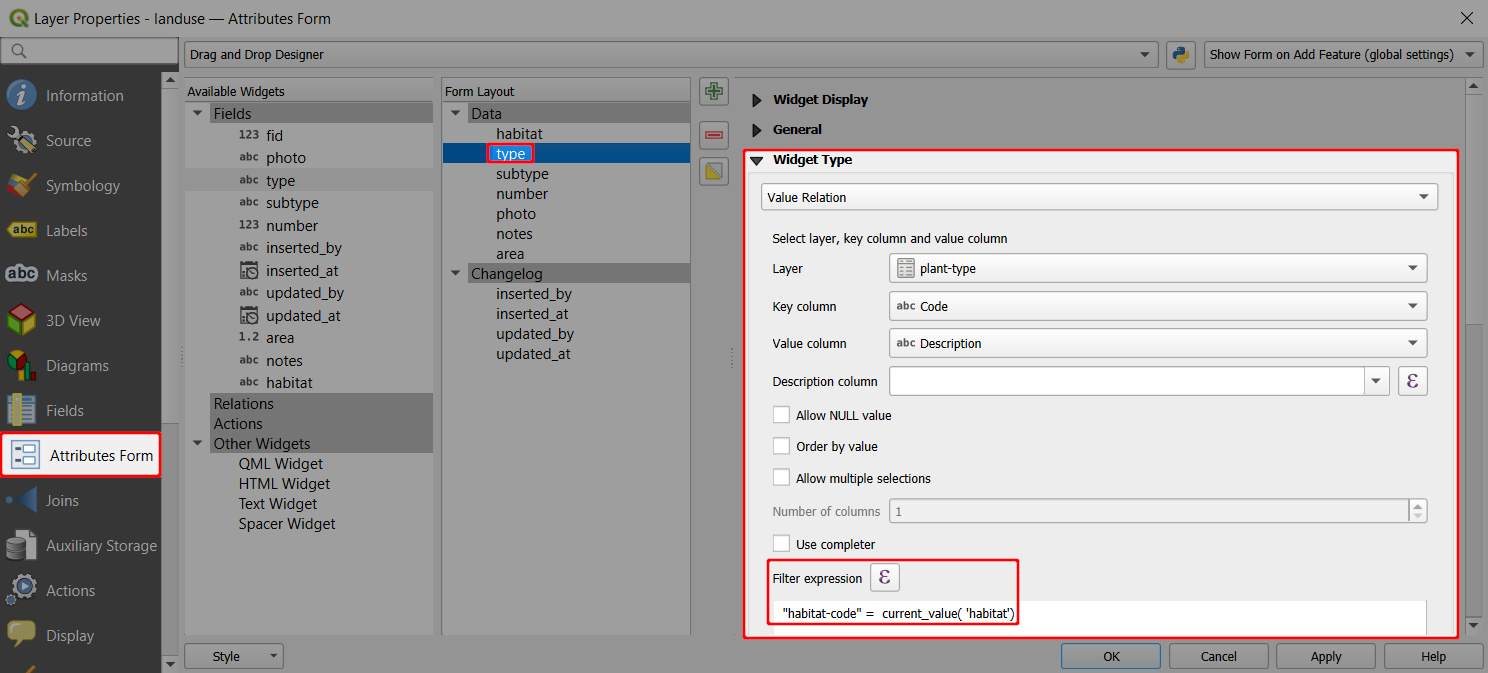
- Key column is the field that contains the values (here:
Likewise, the
subtypefield (aliased as Plant type) uses the Value relation widget with values defined in theplant-sub-typetable:- Key column is the field that contains the values (here:
id) - Value column is the field that contains the alias (description) of the value (here:
Species) - Filter expression:
"Code" = current_value('type')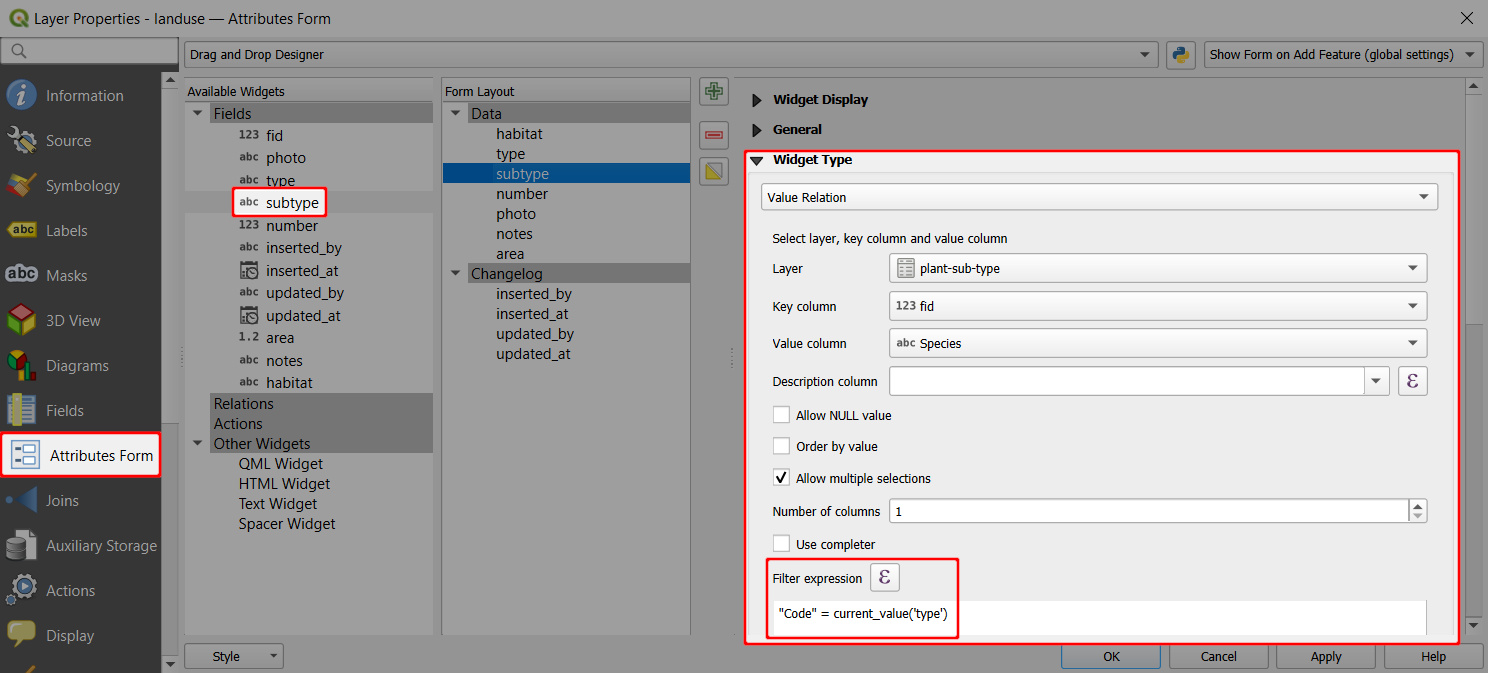
- Key column is the field that contains the values (here:
And this is how the drill-down form looks in the mobile app. After selecting Land use: Farmland, the Type field only offers values Cereals, Oil plants or Vegetables. After selecting Cereals, the Plant type offers only relevant options such as Wheat, Rye or Barley.